Supply Chain Management
The Company sees suppliers as our important partners. We are committed to building mutual trust and a stable sustainable supply chain, as well as flourishing businesses together with our suppliers. The Company assesses suppliers against the criteria, namely Quality, Cost, Delivery, Service, and Sustainable Risks, by using our business influence to demand that they disclose sustainability information and improve their sustainability performance.
Four Major Principles of Supply Chain Management
Upholding the spirit of accountability, the Company has built a responsible supply chain in accordance with the four major principles of supply chain management, namely Code Compliance, Risk Assessment, Auditing Programs, Continuous Improvement, and Implementation of Responsible Supply Chain Management of all purchase contracts the Company have signed with suppliers, the Company stipulates thereon that suppliers comply with the "Code of Conduct- Responsible Business Alliance, RBA". We also demand that tier 1 suppliers who meet the criteria set forth by the Management Production Department and the Procure Department fill out the "Sustainable Risk Assessment Questionnaire", the contents of which covering five aspects, namely Labor, Occupational Health and Safety, Environmental Protection, Supply Chain Management, and Sustainability and Risk Management. The Company's personnel will review the questionnaire and grade the suppliers into different sustainability risk level according to their scores. The Company then performs supply chain management and optimization according to their long-term sustainability performance. New suppliers also need to pass basic corporate social responsibility assessment (the assessment content including human rights, occupational health and safety, and environmental management); only after they pass the assessment are they allowed to do business with the Company. Subsequently, they also need to fill out the "Sustainability Risk Assessment Questionnaire". 100% of the new suppliers are screened against environmental standards and social criteria.Of all purchase contracts the Company have signed with suppliers, the Company stipulates thereon that suppliers comply with the "RBA Code of Conduct". We also demand that suppliers who meet the criteria set forth by the Production Management Department and the Procurement Department fill out the "Sustainability Risk Assessment Questionnaire", the contents of which covering five aspects, namely Labor, Occupational Health and Safety, Environmental Protection, Supply Chain Management, and Corporate Governance. The Company's personnel will review the questionnaire and grade the suppliers into different sustainability risk level according to their scores. The Company then performs supply chain management and optimization according to their long-term sustainability performance. In 2024, a total of 111 suppliers underwent environmental and social impact assessments through the "Supplier/Contractor Sustainability Risk Assessment Questionnaire." Among them, 7 suppliers were identified as having significant actual or potential negative impacts on the environment or society. The main negative impacts were failure to establish occupational safety and health management systems, environmental management systems, and failure to implement organizational carbon inventories. The procurement department will continue to monitor the improvement status of non-compliant suppliers over the next 2 years. The percentage of relationships terminated after evaluation this year is 0%.
At the same time, the Company considers factors such as procurement amount, delivery batches, and supply nature to screen out critical suppliers10 based on risk identification results. Critical suppliers must cooperate by signing the "RBA Supplier Code of Conduct" (with a 100% code of conduct signing rate) and accept annual RBA audits conducted by the Company's professional staff. In 2024, to align with the revision of RBA standards, the Company updated the Supplier Code of Conduct. Furthermore, the Company emphasizes improving suppliers' sustainability management capabilities. Through RBA audit explanations and training courses, we educate suppliers on prohibiting child labor, human rights, anti-discrimination/anti-harassment, health and safety, pollution and greenhouse gas management, anti-corruption, grievance channels, privacy, management systems, material restrictions, and responsible mineral sourcing, deepening sustainability awareness throughout the supply chain. In 2024, 57 suppliers participated in the annual supplier education and training courses.
The company considers factors such as purchase amount, delivery batch number and nature of supply, and selects first-tier suppliers who must cooperate in signing the "Supplier Code of Conduct".In order to continue to improve the sustainability awareness of the supply chain, the company revise the supplier code of conduct in 2023 and require qualified suppliers to resign the code of conduct (the code of conduct signing rate is 100%). In addition, the company held a supplier meeting in 2023, using RBA VAP version 7.1 as the basic teaching material, supplemented by Phison’s important sustainability policies, to communicate ESG principles and regulation with suppliers and contractors(the communication topics covering human rights, anti-discrimination/anti-harassment, health and safety, Pollution and greenhouse gas management, anti-corruption, grievance channels, privacy, management systems, material restrictions and responsible sourcing of minerals, etc).

Corresponding sustainability standards that suppliers at all levels should meet
Purchasing Department and Production Control Department should prepare and regularly check the "QR2303 Main Supplier List" every year. The inventory can be based on annual expenditure, key components of core business, multiple procurement, within the supply chain of the ICT (Information and Communication Technology) industry, etc.
Raw material suppliers are divided into A Level, B Level and C Level based on the total purchase amount and continuing transaction amount. Sub-contractors are classified into A Level and B Level based on production volume and whether they are customer designated processing factory. The sustainability standards that suppliers at all levels of the Purchasing Department and Production Management Department should meet are as follows:
| Grading | Sustainable standards |
| A level | Obtain ISO 14001 certificate |
| Obtain ISO 14064-1 certificate | |
| Obtain ISO 45001 certificate | |
| Fill out the "QR0654-A Supplier/Subcontractor Sustainability Assessment Questionnaire" every year | |
| B or C level | Fill out the "QR0654-A Supplier/Subcontractor Sustainability Assessment Questionnaire" every year |
Supplier Audit
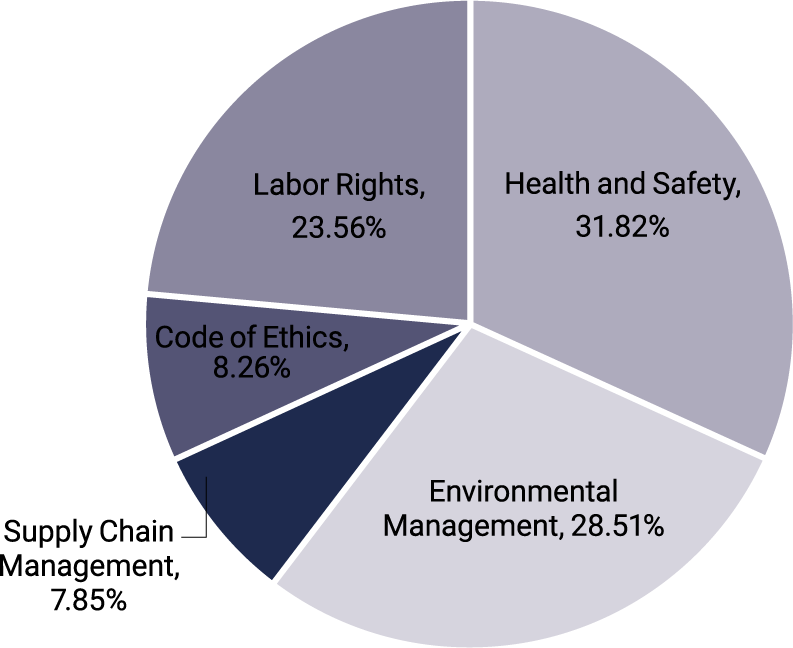
To reduce the sustainability risk in our supply chain, the Company has established the "RBA Vendor Management Policy", with an annual audit being conducted on all of our critical suppliers11 with respect to labor rights, health and safety, environmental management, code of ethics, and compliance and effectiveness of their supply chain management. A total of 22 critical suppliers were audited on-site this year. The remaining critical suppliers have all obtained RBA VAP certification, so they only need to provide third-party reports for documentation audit. Auditors will promptly inform the supplier of any defects found during their audits. The defects will then be reported to the department head and the supplier will be asked to provide an improvement plan; furthermore, the supplier will be required to submit the improvement plan containing corrective actions within one week.
The overall audit pass rate in 2024 was 77.08%, with 242 deficiency items identified. The main causes of deficiencies were excessive overtime, zero-fee recruitment for migrant workers, and environment-related issues. The Company's audit representatives have communicated the audit findings and discussed possible improvement plans with each supplier. The Company did so because according to the management regulations, the Company's audit representatives and the supplier may agree on a deadline for improvement completion. If the supplier fails to improve before the deadline, the Company will reduce or suspend the orders to be placed with it, or remove it from the List of Approved Suppliers.
Defect Analysis for Supplier Audit
Metal Raw Materials
The Company has calculated the metal usage and recycling ratio in 2024 for major suppliers in PCB, Connector and structural components. The results are as follows.
| Item | Recycled material weight(t) | Total Amount(t) | Recycled proportion |
| Aluminum (Al) | 4.15 | 658.84 | 0.63% |
| Stainless steel | 0.00189 | 0.88 | 0.21% |
| Copper (Cu) | 578.66 | 912.22 | 63.43% |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0 | 2.30 | 0.00% |
| Gold (Au) | 0.000048 | 0.39 | 0.01% |
| Iron | 0 | 38.19 | 0.00% |
